The Best Time to Take Magnesium
- Magnesium is an essential mineral that support’s the body’s functioning.
- There are a wide variety of magnesium-rich foods, such as oats, spinach, avocado, dark chocolate and bananas.
- Magnesium supplements provide many health benefits and help prevent magnesium deficiency.
Behold, magnesium, the MVP of supplements. But, “When is the best time to take magnesium?”
This important mineral has been supporting more than 300 functions in the body since you were born, but it’s only been getting the recognition it deserves as of late. Some of its most celebrated benefits include energy production, promoting better sleep, and supporting nerve and muscle function.[1]
If you’ve recently started taking a magnesium supplement, some questions have likely crossed your mind, such as “Should I be eating foods with magnesium, too?” Keep reading to learn the answers to these important questions.
What is Magnesium?
Magnesium is an essential mineral that’s required for the body to function. It supports crucial processes of the body such as stimulating energy production, regulating blood sugar, and supporting nerve and muscle function.[2]
But how much magnesium should you be getting each day? According to the National Institutes of Health, the recommended intake is 310–320 mg of magnesium per day for women and 400–420 mg of magnesium per day for men.
The best time to take magnesium supplements is entirely up to you. It could be first thing in the morning with a cup of coffee or at night right before bed. Research has shown that long-term use of magnesium is the key to its effectiveness, not timing. Just focus on creating a consistent routine.
Benefits of Magnesium

From improving exercise performance to giving you a steady stream of energy to helping you sleep at night, here are some of the most recognized health benefits of magnesium:
Improves Exercise Performance
Magnesium has been found to prevent muscle cramps, so you never have to skip leg day – or any gym day for that matter. It also increases overall power in your workouts.
One study of more than 2,500 women found that higher intakes of magnesium resulted in increased muscle mass and power.[3]
Boosts Energy
Magnesium and energy go hand in hand since magnesium creates ATP, an organic compound that provides energy to the muscles. This does the body good by ensuring that you feel less sluggish throughout the day.
Manages Blood Sugar
Several studies have looked at magnesium’s role in regulating blood sugar (glucose), the body’s main energy source.
In a 12-week study of 54 people with type 2 diabetes, researchers found that a daily intake of 300 mg of magnesium lowered glucose levels, including right after a meal.[4]
Magnesium also is essential for carbohydrate metabolism and insulin secretion. Another study found that getting enough magnesium daily may prevent type 2 diabetes by 22 percent.[5]
Provides Restful Sleep

Get some restful sleep with magnesium. Magnesium is responsible for awakening GABA, a neurotransmitter that relaxes the mind and helps you sleep. That is why many opt to use magnesium in the place of other sleep aids, like melatonin.[6]
Foods with Magnesium

Magnesium is found in a large variety of foods, such as leafy green vegetables, whole grains, legumes and beans and more.
It’s estimated that 15 to 20 percent of people in developed countries are magnesium deficient.[7] This is when the amount of magnesium in the blood is below normal.
Signs of magnesium deficiency:
- Muscle twitches
- Muscle cramps
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- High blood pressure
- Loss of appetite[8]
Only 52% of Americans got enough magnesium from food between 2013 to 2016, according to the National Institutes of Health.
To ensure you don’t become another statistic, try adding these magnesium-rich foods into your diet:
- Green leafy vegetables, such as spinach, kale, Swiss chard, collard greens
- Whole grains, such as oats, wheat, buckwheat, barley
- Fruits, such as avocado, apple, banana
- Vegetables, such as broccoli, carrots
- Dairy, such as milk and yogurt
- Nuts, such as Brazil nuts, cashews, almonds, peanuts
- Seeds, such as pumpkin seeds, flax seeds, chia seeds
- Legumes, such as chickpeas, black beans, lentils, soybeans
- Meat, such as chicken, beef
- Fish, such as salmon, halibut, tuna
- Others, such as tofu, soy milk and dark chocolate
Supplementing with Magnesium
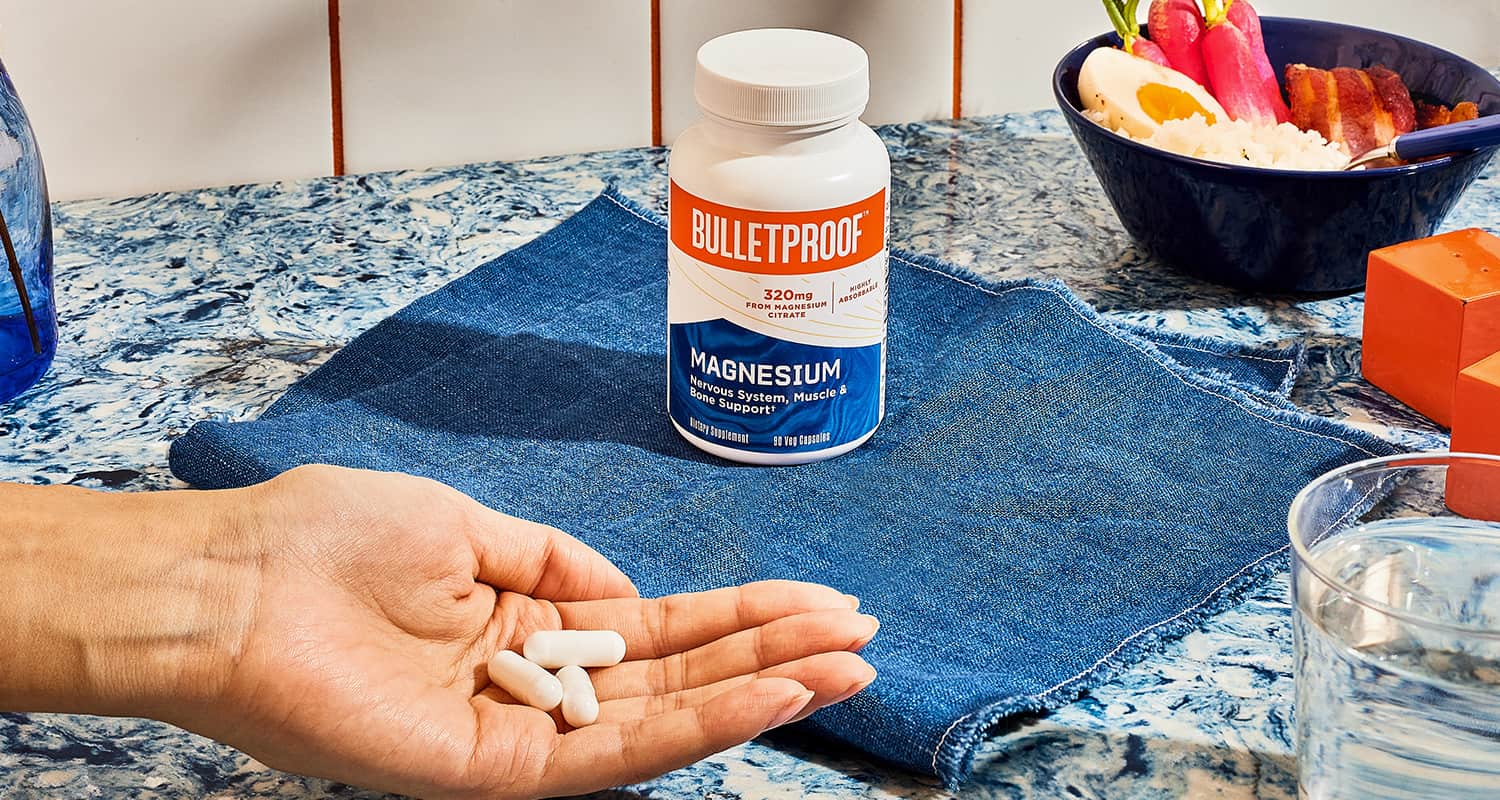

Struggling to get magnesium in your diet? A magnesium supplement can help by filling in the gaps that your body needs to function at its best. These come in many forms — capsules, powders and liquids — as well as many different types.
Magnesium citrate, magnesium oxide and magnesium glycinate are some of the most common.
Regular intake of magnesium supplements is linked to many health benefits, such as keeping the heart healthy.
A meta-analysis of 34 studies found that taking 350 mg of magnesium each day for approximately three months reduced both systolic and diastolic blood pressure by 2 mm and 1.78 mm Hg, respectively.[9]
Magnesium supplements are also crucial to take if you have a health condition that puts you at greater risk for magnesium deficiency. This includes type 2 diabetes, Crohn’s disease or alcoholism.[10]
Choosing the right magnesium supplement doesn’t have to be a chore. Bulletproof Magnesium is a science-based product that contains 320 mg of magnesium citrate, the most absorbable form of magnesium. It soothes the mind by relaxing the nervous system and offers support to the bones and muscles.
While magnesium supplements are generally safe to take, some people may experience some mild side effects. These include:
- Upset stomach
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
Taking your magnesium with food (including the magnesium-rich foods we talked about) may help prevent some of these adverse effects.
Magnesium is an essential mineral that the body needs to remain healthy.
It provides a large variety of benefits, such as improved heart health, stronger bones and reduced muscle cramps. You can get magnesium through two different avenues: food sources and supplements.
As it turns out, the timing of when you take magnesium doesn’t really matter; what’s most important is that you take it consistently for a long time to reap the maximum benefits.
Sign up for early access to sales, product launches, the latest Bulletproof news and more!



